Dujiangyan is a world cultural heritage (inscribed in the "World Cultural Heritage" list by UNESCO in 2000), a world irrigation engineering heritage, a national key cultural relic protection unit, a national scenic spot, and a national AAAAA-level tourist attraction.
Dujiangyan is located in the west of Dujiangyan City, Chengdu City, Sichuan Province, on the Minjiang River in the western part of the Chengdu Plain. It was built in the last year of King Qin Zhao (approximately 256 BC to 251 BC), and was excavated by the predecessor Li Bing and his sons of Shu County. The large-scale water conservancy project organized and constructed on the basis of the water diversion fish mouth, Feisha weir, Baopingkou and other parts, has been playing the role of flood control and irrigation for more than two thousand years, making the Chengdu Plain into a flood and drought, a fertile land for thousands of miles. The "land of abundance", the irrigation area has reached more than 30 counties and cities, covering an area of &4u:200b&4u:200bnearly 10 million acres. It is the oldest, only remaining, still in use, and grand water conservancy project characterized by non-dam diversion in the world so far. It is the crystallization of hard work, bravery and wisdom of the working people in ancient China.
Dujiangyan Scenic Area mainly includes Fulong Temple, Erwang Temple, Anlan Cable Bridge, Yuleiguan, Lidui Park, Yuleishan Park, Yunvfeng, Lingyan Temple, Puzhao Temple, Cuiyue Lake, Dujiangyan Water Conservancy Project, etc.
On November 18, 2020, it was elected as the "New Landmark of Bashu Cultural Tourism Corridor".
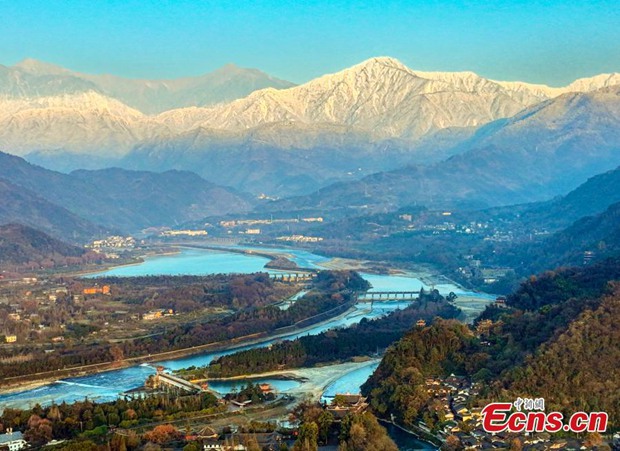
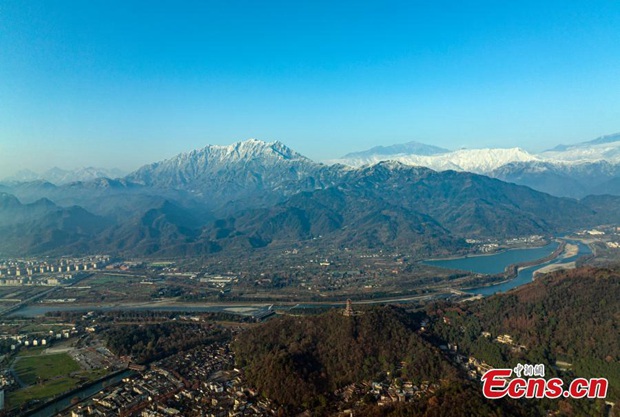



Photo taken on Dec 29, 2021 shows Dujiangyan irrigation system at the foot of a snow-capped mountain, the west part of Chengdu Plain, southwest China's Sichuan province. (China News Service/Chen Xianlin)